Art.AI
Team members: Maika Nishiguchi, Seho Kwak, and Rachel Yang

Abstract
In this project, we present a novel approach to neural style transfer for creating visually appealing baby portraits by combining two different artistic styles. By splitting the input image into two halves and applying distinct styles to each half, we aim to generate a unique and engaging output. Our approach leverages the power of convolutional neural networks (CNNs), specifically the VGG19 architecture, to extract content and style features from the input images and generate the stylized output.
We implement our neural style transfer algorithm using the PyTorch framework and utilize VGG19’s pretrained model to extract the features necessary for content and style representation. The content and style losses are computed using the mean squared error between the respective feature representations in the input and generated images. The optimization process is carried out using the L-BFGS optimization algorithm, which iteratively updates the input image until convergence.
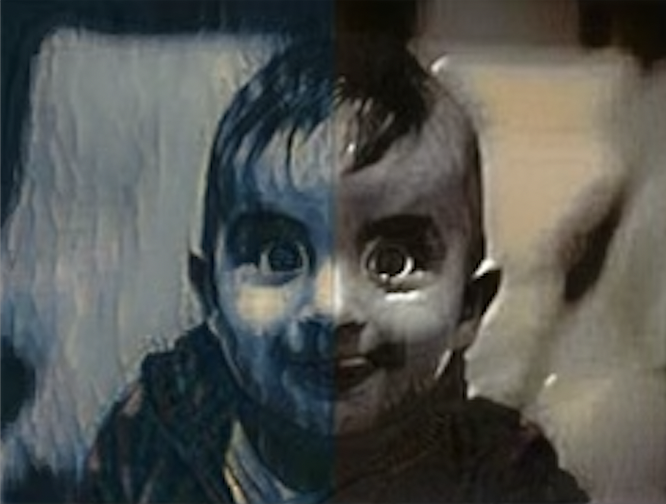
In our implementation, we first split the content image (baby portrait) into two halves. We then apply two different artistic styles to the left and right halves of the content image. The final output is obtained by merging the stylized left and right halves to form a single image that seamlessly combines the two styles.
To evaluate the effectiveness of our approach, we showcase results obtained from applying our neural style transfer algorithm to several baby portraits. The outputs demonstrate the successful combination of the two distinct artistic styles, resulting in visually engaging and unique baby portraits. We also provide intermediate results at different stages of the optimization process, illustrating the gradual evolution of the generated images. By showing images after various steps, such as 10 and 500, we offer insights into how the neural style transfer algorithm refines the output over time.
Future work could involve applying different artistic styles to various parts of the image or different shapes instead of just splitting it in half, as done in our project. Additionally, we could explore other applications of neural style transfer beyond baby photos, such as video or 3D models, to further extend the capabilities and applications of this technique. Overall, our project contributes to the growing body of research in neural style transfer and showcases its potential for creating captivating, personalized artwork.
Introduction & Related Works
Neural style transfer is a captivating and rapidly expanding area of research in computer vision and graphics. This technique involves transferring the style from one image to another, essentially blending the content of a target image with the style of a source image. The process can be viewed as a texture transfer problem, where the goal is to synthesize a texture from the source image while preserving the semantic content of the target image. An example of neural style transfer can be seen in Gatys et al. (2016)1, where the style of famous paintings is applied to various photographs, as shown in the images below (Figure 1).
A successful style transfer algorithm should extract the semantic content of the target image, such as objects and general scenery, and use this information to guide a texture transfer process that renders the content in the style of the source image. This requires the algorithm to (1) recognize objects in the target image and (2) recombine the objects and style of the source image.
 Figure 1. Images that combine the content of a photograph with the style of several well-known artworks. Source: Gatys et al. (2016).
Figure 1. Images that combine the content of a photograph with the style of several well-known artworks. Source: Gatys et al. (2016).
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have emerged as the most popular method for achieving this task. Gatys et al. (2016)1 demonstrated the use of image representations from CNNs optimized for object recognition to transfer the style of a reference image onto an input target image. Similarly, Li et al. (2021)2 explored how CNNs can be applied to process 2-D images, including object detection and image classification. Luan et al. (2017)3 built upon this approach by augmenting the algorithm to achieve more photorealistic style transfer while minimizing distortion. Additionally, Kotovenko et al. (2019)4 introduced a content transformation module between the encoder and decoder to reduce extra deformations, additions, and deletions of content details, learning how style influences content details and generalizing this to other class details.
For our project, we will use baby photos from the dataset as content images and famous artworks from another dataset as style images. We will start by replicating the neural style transfer tutorial available on the PyTorch website and adjust the parameters to train our model using the chosen datasets. Our primary focus will be on baby photos, applying different art styles to these images.
Our goal is to split one photo in half, applying two different art styles to each half of the image. We will experiment with blending multiple styles into the output image and apply each style to different regions of the image.
Methods
We employed PyTorch as the primary software for our neural network implementation, taking advantage of its flexibility and efficiency in building and training models. Using the baby photos dataset as our content images and the best artworks dataset for style images, we created a unique dataset tailored to our project’s goals.
In this study, we utilized the pre-trained VGG19 convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture available in the PyTorch library. The VGG19 model consists of 16 convolutional layers, 5 max-pooling layers, 3 fully connected layers, and 1 softmax layer. We chose VGG-19 for its performance and ease of use in extracting features for style transfer.
Our inputs consisted of three-channel images represented as matrices of pixel values, which the model used to extract content and style information. The output of our neural style transfer model was a visually appealing image that fuses the style of two different images with the content of a baby photo. This three-channel image, with the same shape and type as the input image, was intended to produce an aesthetic result rather than serve any specific classification, regression, or segmentation task.
We modified the PyTorch tutorial code to create an output image where each half has a different style, by implementing the following changes:
- Load the two style images separately using the
style_image_loaderfunction.def style_image_loader(image_name): image = Image.open(image_name) image = loader(image).unsqueeze(0) return image.to(device, torch.float) - Split the content image into two halves using the
split_imagefunction, which returns the left and right halves of the input image.def split_image(image): width, height = image.size half_width = width//2 left_half = image.crop((0, 0, half_width, height)) right_half = image.crop((half_width, 0, width, height)) return left_half, right_half - Create two separate input images, one for each half of the content image, using the
content_image_loaderfunction.def content_image_loader(image): image = loader(image).unsqueeze(0) return image.to(device, torch.float) - Run the style transfer process independently for each half of the content image using the
run_style_transferfunction, resulting in two separate styled images. - Merge the two styled halves into a single output image using the
merge_imagesfunction, which combines the left and right styled images.def merge_images(left_image, right_image): width, height = left_image.size merged_image = Image.new('RGB', (width * 2, height)) merged_image.paste(left_image, (0,0)) merged_image.paste(right_image, (width, 0)) return merged_image
By making these changes, we created a neural style transfer model capable of generating an output image with each half styled differently, based on two distinct style images.
The following steps outline the complete process:
- Load the content and style images using the
Image.openfunction from the Python Imaging Library (PIL). Resize the images to the desired dimensions using thetransforms.Resizefunction from the PyTorchtransformsmodule. - Preprocess the images by normalizing the pixel values for each color channel (Red, Green, and Blue) and converting the images to tensors using the
transforms.ToTensorfunction. The normalization is necessary because neural networks in the PyTorch library are trained with tensor values ranging from 0 to 1. - Initialize the CNN architecture with pre-trained weights by following the tutorial’s guidelines. In this case, the architecture used is VGG19, a pre-trained convolutional neural network that has proven to be effective for style transfer tasks. Load the VGG19 model using the
torchvision.models.vgg19function, and extract the necessary layers to compute the content and style features. - Define the content and style loss functions using the
nn.Moduleclass from PyTorch. The content loss function quantifies how well the content is preserved in the generated image, while the style loss function measures the preservation of style. The functions are computed based on the Gram matrix, which is used to capture the style information from the style image. The Gram matrix is used to compute the style loss by comparing the correlations between features in the style image and the generated image. It is calculated as the outer product of the feature map’s reshaped matrix. - Split the content image into two halves using the
split_imagefunction, and initialize two separate input images using thecontent_image_loaderfunction. - Optimize the input images iteratively using the L-BFGS optimization algorithm provided by PyTorch’s
torch.optimmodule. Adjust the pixel values of the input images to minimize the content and style losses. Run the optimization process independently for each half of the content image, with the corresponding style images, using therun_style_transferfunction. We ran the optimization for 300 steps and plotted the loss over time to analyze the optimization process. This results in two separate styled images.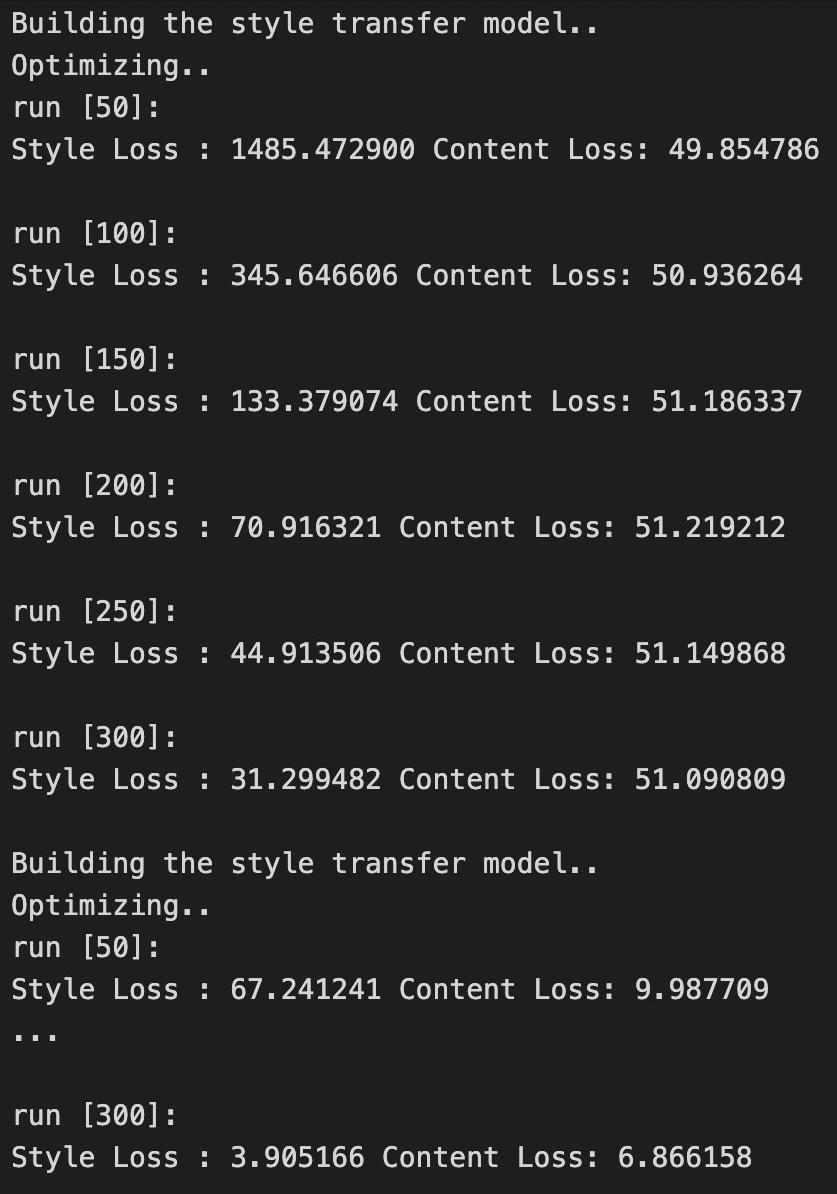
- Merge the two styled halves into a single output image using the
merge_imagesfunction, which combines the left and right styled images. The resulting image will have each half styled differently, based on the two distinct style images. - Convert the output tensor back to a PIL image using the
transforms.ToPILImagefunction, which allows for easy visualization and saving of the generated image. Display the generated image using theimshowfunction and theplt.imshowfunction from thematplotlib.pyplotmodule. - Iterate through the entire baby images dataset, performing the style transfer and merging process for each content image, resulting in a collection of uniquely styled output images.
for baby in baby images: content_image = Image.open(baby) left_half, right_half = split_image(content_image) left_img = content_image_loader(left_half) right_img = content_image_loader(right_half) input_left_img = left_img.clone() input_right_img = right_img.clone() style_left = run_style_transfer(cnn, cnn_normalization_mean, cnn_normalization_std, left_img, style_img_1, input_left_img) style_right = run_style_transfer(cnn, cnn_normalization_mean, cnn_normalization_std, right_img, style_img_2, input_right_img)This method allows you to create a new image that combines the content of a baby photo with the styles of two distinct artworks, applied to each half of the image. The resulting images are visually appealing and showcase the ability of neural style transfer to create compelling artwork inspired by a diverse range of styles.
Discussion
In this project, we aimed to create a unique application of neural style transfer by blending two different art styles in each half of a baby photo. We started with the PyTorch neural style transfer tutorial, which uses a pre-trained convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture to transfer the style of a reference image onto an input target image. We then modified the code to achieve our specific goal of applying multiple styles to one image.
Our results showcase the visual appeal and effectiveness of blending two distinct art styles in a single image, specifically when applied to baby photos. We have evaluated the quality of the style transfer by examining several aspects: the preservation of content from the original image, the accurate representation of both art styles, and the seamless integration of the two styles in the output images. To better understand and explain our evaluation, we have included example videos and images. These videos allow for a direct comparison between the original content and style images and the final results, highlighting the successful combination of different art styles in a single output image. We also showcased how the output images evolved during the optimization process by displaying images after multiple steps, ranging from 10 to 500. Our approach effectively demonstrates the ability to blend two styles seamlessly in a single output image. Example images can be found below to support our evaluation
By building upon the PyTorch tutorial and incorporating custom datasets for content and style images, we have contributed to the growing body of research in neural style transfer and demonstrated the potential of exploring diverse applications in this area.
Baby Image
Style Images
Output Image!
10 steps

50 steps

100 steps

500 steps

Web App Demo
In these videos, we show a demo of our code and web app!
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/98056010/235505188-b50fe4c6-7e92-4223-8e9f-52228460d38e.mov
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/98056010/235505437-80043370-6c9e-4ba9-a2c6-8f6680d93767.mov
Ethics Discussion
While our project focuses on the artistic aspect of neural style transfer, it is essential to consider the ethical implications that may arise from using this technology. One area of concern is the potential for copyright infringement when using and modifying existing artworks or photographs. As we utilize famous artworks from various artists for our style images, we must ensure that we are respecting their intellectual property rights and acknowledging their contributions. It is also crucial to obtain permission from the owners of the baby photos used as content images, as these images involve personal data and may be subject to privacy concerns.
Another ethical consideration is the potential misuse of neural style transfer for creating misleading or manipulative images. By blending different styles and altering the content of an image, the technology could be exploited to generate deceptive or malicious content, such as deepfake images or misinformation. It is the responsibility of researchers and developers to create guidelines and implement safeguards to prevent such misuse of the technology.
Lastly, it is crucial to consider the cultural implications of blending artistic styles from different origins. The merging of styles from various cultures and time periods could be seen as a celebration of diversity and creativity. However, it is essential to approach this process with cultural sensitivity, ensuring that the final output does not inadvertently misrepresent or appropriate cultural elements in a disrespectful manner. By considering these ethical concerns, we aim to contribute to the responsible development and application of neural style transfer technology.
Reflection
Reflecting on our work, there are a few things we would do differently next time. First, we would explore additional methods for blending multiple styles in the output image, such as incorporating more sophisticated algorithms or incorporating the use of deep learning techniques. This could potentially lead to more visually appealing results and better preservation of content and style.
In addition to these improvements, we also envision integrating more advanced user interaction capabilities into our web application. This could include allowing users to manually select regions of the content image to apply different styles, or even offering a brush tool for painting the styles directly onto the image. Such features would provide users with greater control over the final output, enabling them to create truly personalized and unique art pieces.
Furthermore, we would like to expand our project by exploring other applications of neural style transfer beyond baby photos. There are many potential avenues for research, such as applying neural style transfer to video or 3D models, which could lead to exciting new developments in the field.
Overall, our project demonstrates the potential of neural style transfer for creating visually appealing images with unique artistic combinations. By building on existing research and exploring new applications, we contribute to the growing body of knowledge in this exciting field.
References
-
Gatys, L. A., Ecker, A. S., & Bethge, M. (2016). Image style transfer using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 2414-2423). ↩ ↩2
-
Li, Z., Liu, F., Yang, W., Peng, S., & Zhou, J. (2021). A survey of convolutional neural networks: analysis, applications, and prospects. IEEE transactions on neural networks and learning systems. ↩
-
Luan, F., Paris, S., Shechtman, E., & Bala, K. (2017). Deep photo style transfer. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 4990-4998). ↩
-
Kotovenko, D., Sanakoyeu, A., Ma, P., Lang, S., & Ommer, B. (2019). A content transformation block for image style transfer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 10032-10041). ↩